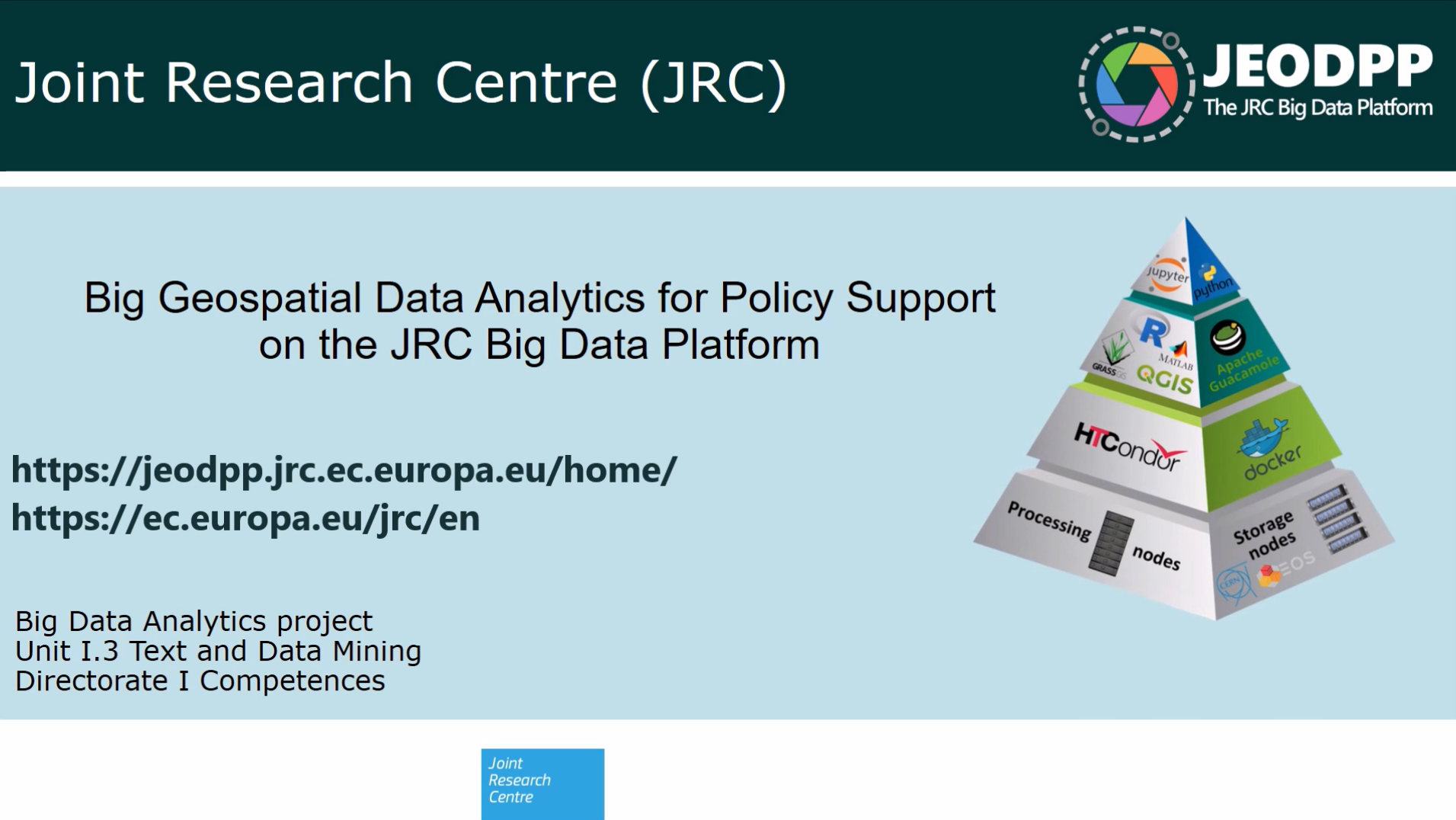
Vision
The JRC Big Data Analytics Platform (BDAP) links data, data services, data scientists and thematic experts for generating policy relevant insights and foresight. It will play an instrumental role in advancing JRC to better mobilise and synthesise its collective knowledge and expertise in support to the EC priorities.
Building blocks
BDAP is build around a petabyte-scale storage system coupled with a processing cluster, accessible from anywhere through encrypted protocols and multi-factor authentication. It provides interactive data analysis tools, a remote data science desktop and distributed computing with specialized hardware for machine learning and deep learning tasks. It groups services for data analytics, data visualisation and data dissemination under the same platform.
Main services
All the BDAP services are built on top of the hardware layer, which consists of servers dedicated to storage and servers dedicated to processing. The multi-petabyte storage is managed by EOS, the distributed file system created by CERN, that allows all the services to see the full storage capacity as a single volume. Dedicated hardware for machine learning and deep learning is also available. On top of the hardware layer, three main services are built, as displayed in the following image:
Quick guide
A quick guide to BDAP and its services is available for downloading at the following link:
BDAP services requiring authentication are mainly serving JRC users. Please consult the JRC Service Catalogue for the Big Data Analytics Platform for more information.
Documentation
User documentation on authentication methods and how to access BDAP platform
AuthenticationUser guide of the pyjeo library: how to manage geospatial data in JEO-desk and JEO-batch
User guide of the interapro library: how to visualise and analyse geospatial datasets in the JEO-lab Jupyter notebooks
User guide of the vois library: library to simplify the development of impactful web applications as Voila' dashboards
Links to help pages of the main libraries to use to create graphical user interface elements in Jupyter notebooks and Voilà dashboards:
- Widgets GUI elements:
- ipywidgets ipyvuetify vuetifyjs
- Mapping:
- ipyleaflet
- Tabular data:
- qgrid
- Charting:
- bqplot plotly bokeh matplotlib
- Custom drawing:
- ipycanvas
- Hierarchical data display:
- ipytree
- Events management:
- ipyevents
How to access the platform
Access to BDAP services requires users to have a BDAP account. Registration is restricted to the Joint Research Centre and its contractors and partners. The access to the registration page requires to have already an EU-Login account.
Services
List of services provided by the JRC Big Data Analytics Platform:
Quick access to BDAP servicesThe JEO-lab is a Jupyter notebook environment, intended primarily to interactively analyse and visualize data via a dedicated API. In addition to the usage of the API, JEO-lab is also used for starting up machine learning notebooks or accessing project-specific notebook containers for selected use cases. JEO-lab documentation
The JEO-desk is a desktop terminal service that provides a graphical Linux remote desktop terminal (Xubuntu based) accessible from within a modern web browser with support for HTML5. This virtual terminal is provided from machines located within the JEODPP infrastructure and therefore with fast connection to the JEODPP data. JEO-desk documentation
The JEO-batch service provides computing power to the JRC experiments for tasks such as high scale image processing, data analysis and simulation. It is an advanced, distributed system designed mainly for high-throughput scientific computing. JEO-batch documentation
The JEO-cloud service is based on Nextcloud and is aimed at facilitating collaboration between JEODPP users and making easier the transfer of documents (scripts, project files etc.) and small datasets between the user personal computer and the JEODPP Terminal Service. It also provides some functionalities useful to provide remote support to JEODPP users by the JEODPP team (screen sharing and videoconferencing). JEO-cloud documentation
Voilà is a Jupyter notebook extension to automatically create standalone applications and dashboards. Notebooks are rendered by showing only the output of the cells, while the code is hidden. Suitable for non-technical experts for communicating insights and foresight to a wider audience. Single environment for full data analytics workflows from research and innovation to outreach engaging policy makers and citizens.
As an example of a Voilà dashboard, the CollectionsExplorer is a good starting point to explore the geospatial datasets stored in the platform.
GitLab is the DevOps platform used at BDAP. It helps BDAP team members and users to collaborate on software development and to provide a place where everyone can contribute. Users can add issues in the BDAP GitLab instance to ask for new features, to evaluate new dataset downloading, to request the installation of new software packages and to report bugs or problems in the BDAP services.
Data
Data provided by BDAP:
Web data catalogue for exploring and browsing all the collections stored in BDAP. It follows the SpatioTemporal Asset Catalog (STAC) specifications providing a common language to describe geospatial data.
Voila' application to browse, visualise and compare the main geospatial datasets available at BDAP.
Geospatial data browser for Web mapping applications using WMS standard and served by the Big Data Analytics Platform. Licenses for service data
Platform information
Timeline
BDAP is the successor of the JRC Earth Observation Data and Processing Platform, widening the scope of the platform towards any type of Big Data analytics. The commonly known name "JEODPP" is continued to be used in most documentations and services URL's. Here a timeline of the project progress:
-
1 January 2015Earth Observation and Social Sensing Big Data pilot projectKick-off of EO&SSBD as a pilot project
-
1 March 2016Purchase and installation of the first hardwareJRC Big Data Platform starts its operativity with the first servers installed and configured
-
1 January 2019Big Data Analytics project launched as an institutional projectJRC Big Data Platform ends the pilot phase and enters full institutional
-
12 December 2020Big Data Analytics Platform recognised as an official EC IT platformEC ITC and Cybersecurity Board (ITCB) provide a positive opinion on the evolution of the platform towards a Big Data Analytics Platform as a component of the EC Data Platform
Numbers
Software stack
The JRC Big Data Analytics Platform is mainly built on Open Source Software. Here a partial list of the tools and libraries used:
Publications
The publications listed here correspond to all publications registered in pubsy and containing at least one co-author from the Big Data Analytics Platform. Numerous publications are the result of fruitful collaborations with other JRC projects and external partners.
Reference publication to be used for citing BDAP in papers:
P. Soille, A. Burger, D. De Marchi, P. Kempeneers, D. Rodriguez, V. Syrris, and V. Vasilev. “A Versatile Data-Intensive Computing Platform for Information Retrieval from Big Geospatial Data”. Future Generation Computer Systems 81.4 (Apr. 2018), pp. 30–40. doi: 10.1016/j.future.2017.11.007.Recent publications:
P. Soille, S. Loekken, and S. Albani, eds. Proc. of the 2023 Conference on Big Data from Space (BiDS’23). ESA-JRC-SatCen. Publications Office of the European Union, Nov 2023. doi: 10.2760/46796 D. De Marchi, A. Burger, F. Eyraud, and P. Soille, “VOIS library: Pushing data science dashboards to the limits,” in Cloud Storage Synchronization and Sharing (CS3 2023), CERN, Mar. 2023, pp. 2–4. [Online]. Available: https://indico.cern.ch/event/1210538/book-of-abstracts.pdf. R. d’Andrimont, M. Claverie, P. Kempeneers, D. Muraro, M. Yordanov, D. Peressutti, M. Batic, and F. Waldner, “AI4Boundaries: An open AI-ready dataset to map field boundaries with Sentinel-2 and aerial photography,” Earth System Science Data, vol. 15 (1), pp. 317–329, 2023. doi: 10.5194/essd-15-317-2023. P. Kempeneers, M. Claverie, and R. d’Andrimont, “Using a vegetation index as a proxy for reliability in surface reflectance time series reconstruction (RTSR),” Remote Sensing, vol. 15 (9), 2023. doi: 10.3390/rs15092303. P. Soille and P. Vogt, “Morphological spatial pattern analysis: Open source release,” The International Archives of the Photogrammetry, Remote Sensing and Spatial Information Science, vol. XLVIII-4/W1-2022, 2022. doi: 10.5194/isprs-archives-XLVIII-4-W1-2022-427-2022. P. Kempeneers, T. Kliment, L. Marletta, and P. Soille, “Parallel processing strategies for geospatial data in a cloud computing infrastructure,” Remote Sensing, vol. 14 (2), 2022. doi: 10.3390/rs14020398. P. Kempeneers, O. Pesek, D. De Marchi, and P. Soille. “A Python Package For The Analysis of Geospatial Data”. International Journal of Geo-Information 8.10 (2019). doi: 10.3390/ijgi8100461Media gallery
-
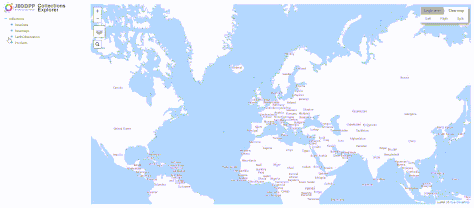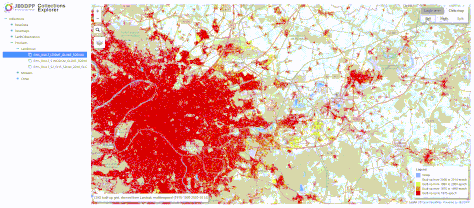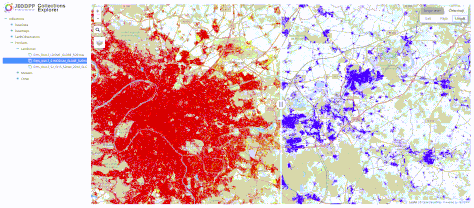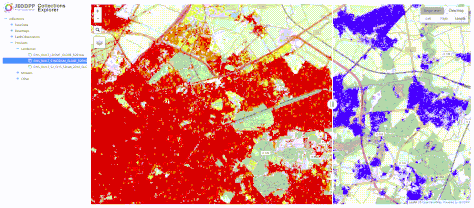
CollectionsExplorer dashboard: browse the tree of JEO-lab datasets and easily compare two geospatial datasets -
Presentation of JEODPP activities for RTD EuroGeoss -

Voilà dashboard on Covid-19 spread in italian provinces -
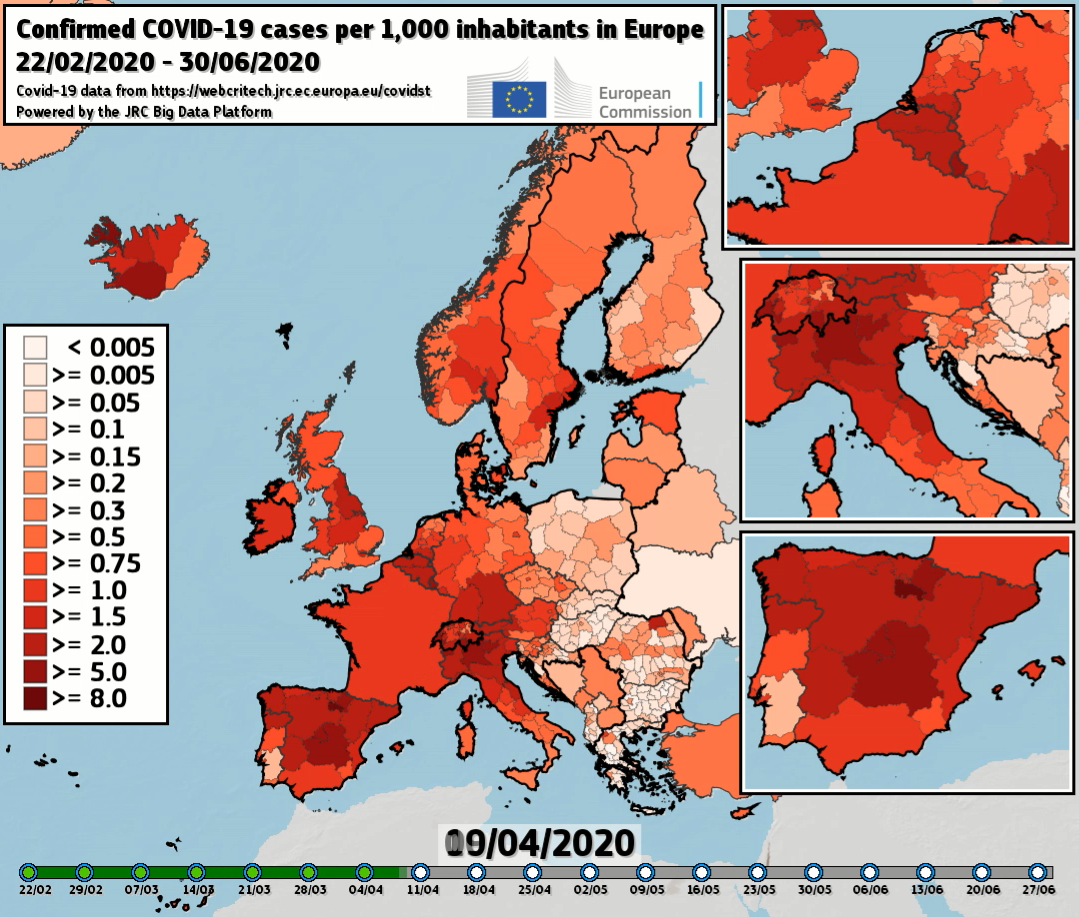
Spread of Covid-19 in the regions of Europe -
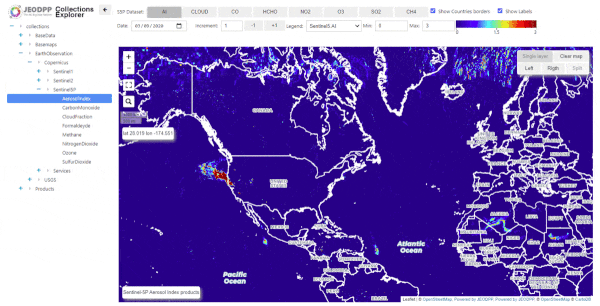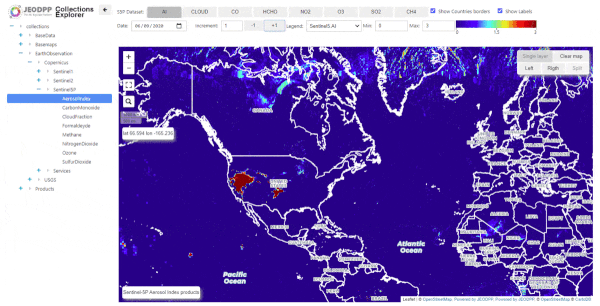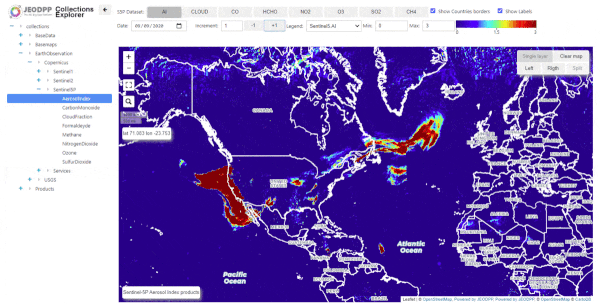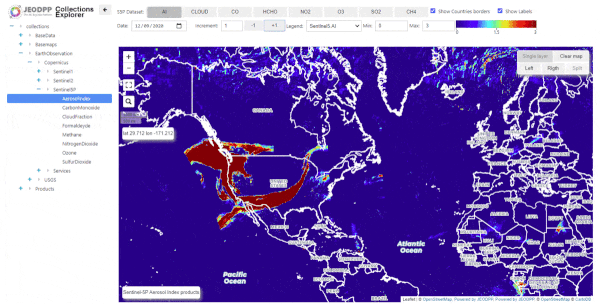
California fires as seen from Sentinel-5P -

Voilà dashboard on EU budget expenditures -

Synthetic view of Covid-19 spread in European countries -

2019 Blue Mountains fires as seen from Sentinel-2 images in s2explorer -

Effects of lockdown measures in NO2 drop in Europe -
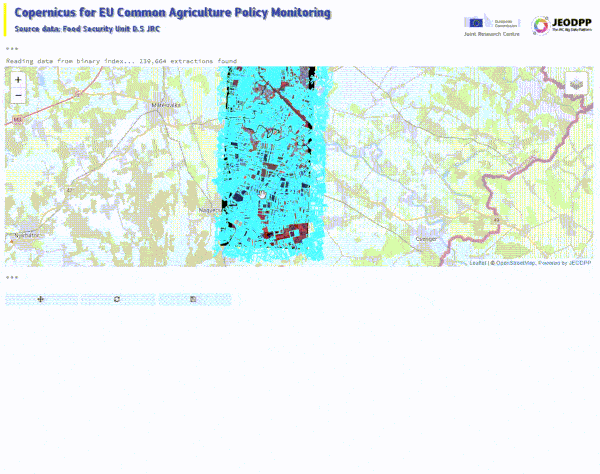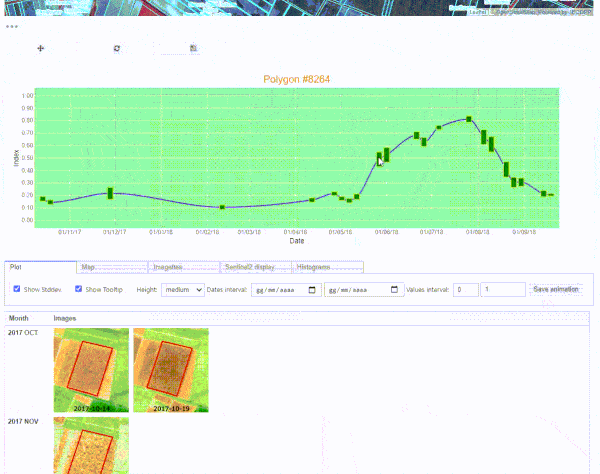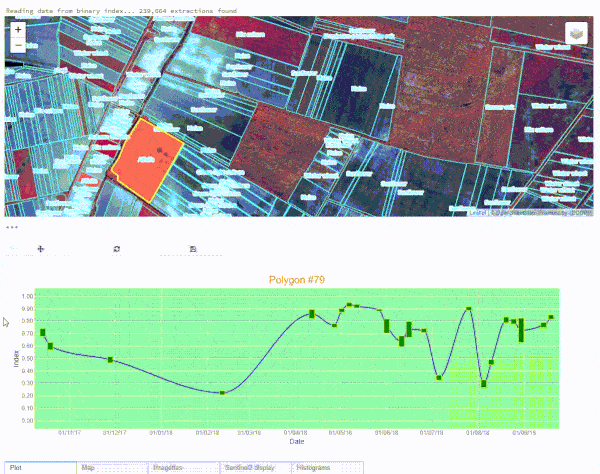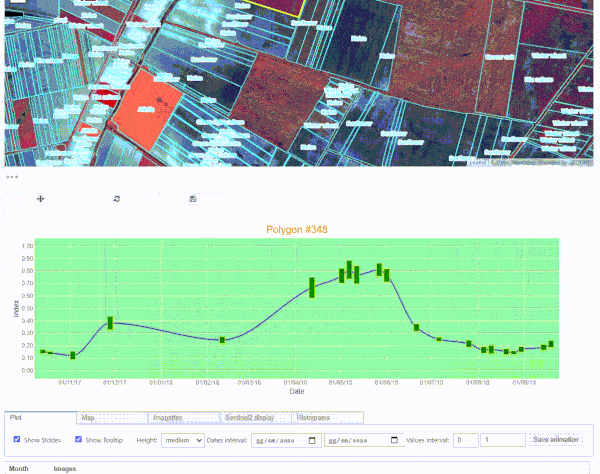
S2explorer application to monitor agricultural parcels
News
Contacts
- Email us
- JRC-JEODPP@ec.europa.eu
- Ask for support
- Create an issue in BDAP GitLab instance
- Follow issues
- by accessing BDAP GitLab instance or by email (reply to GitLab email notifications)
- Request the creation of a use case
- Create a new use case by filling and returning this Excel template
- BDAP Community Teams channel
- BDAP Community Channel on Teams
Team
BDAP is made by people who love IT and Data Science:
- Statutory staff:
- Armin Burger
- Chiara Chiarelli
- Michele Cecotti
- Davide De Marchi
- Paul Hasenohr
- Pieter Kempeneers
- Silviu Onofrei
- Edoardo Ramalli
- Roberto Ugolotti