Video class¶
-
class
inter.Video(format, FilePath, lonmin=0.0, latmin=0.0, lonmax=0.0, latmax=0.0, zoom=0, DelayInMilliseconds=1000, FramesPerSecond=1)¶ Video class is an helper class to create videos. An instance of Video has to be created by giving as argument the format of the video to create (VIDEO_GIF, VIDEO_MP4 or VIDEO_WEBM) and the path of the file to create. Example:
vo = Video(VIDEO_GIF,'output.gif')
On the returned Video object vo, a number of methods can be called, in order to:
set the details of the video creation:
vo.setDelayInMilliseconds(1000) # for GIF output format vo.setFramesPerSecond(5) # for MP4 and WEBM output format vo.setExtentsAndZoom(lonmin,latmin,lonmax,latmax,zoom) # to set the geographic extents of the video vo.setMap(map) # to use current viewport and zoom level of a map to set the geographic extents
define which images have to be overlayed to the video frames:
vo.overlayReset() # Reset the list of images to overlay to the frames vo.overlayAddFile('./logo.png', 4, 4, 190) # Add a PNG file at position (x,y)=(4,4) with opacity=190 vo.overlayAddImage(img, 4, 0, 255) # Add a PIL (Pillow) Image object at position (x,y)=(4,0) with opacity=255
add frames to the video:
vo.addFrame(p) # Add a frame from an :py:class:`ImageProcess` object vo.addFrame([pbBase,p], 5) # Add a frame from a list of overlapped :py:class:`ImageProcess` objects and using 5 dissolved frames to smoothly transit from the previous frame
When the video is complete, a call to
Video.close()is needed to flush the content to the output fileExample of a video created by using the Video class and showing the outbreak of coronavirus in the regions of China on January/February 2020:
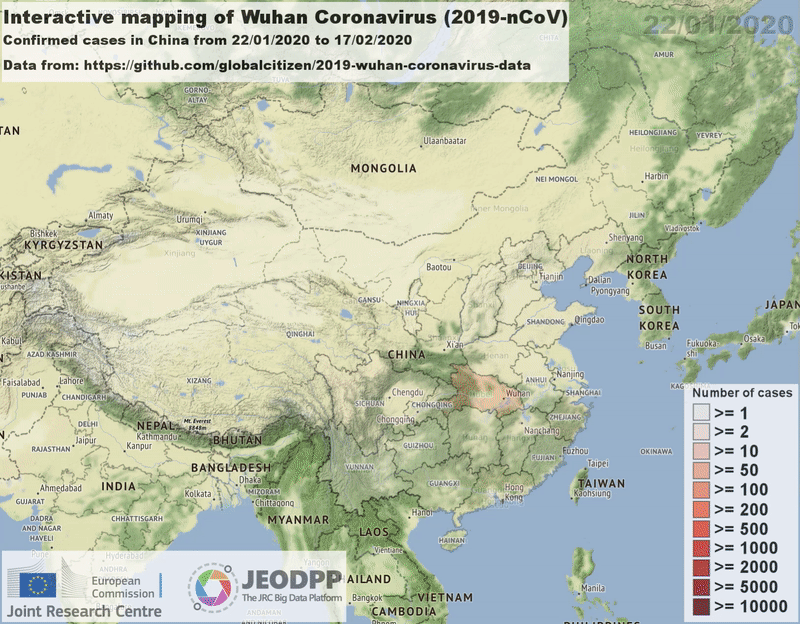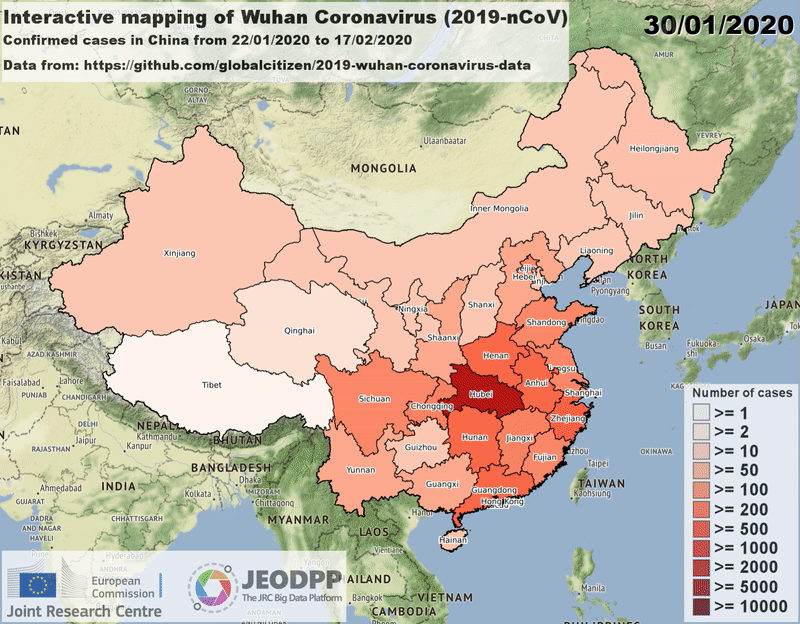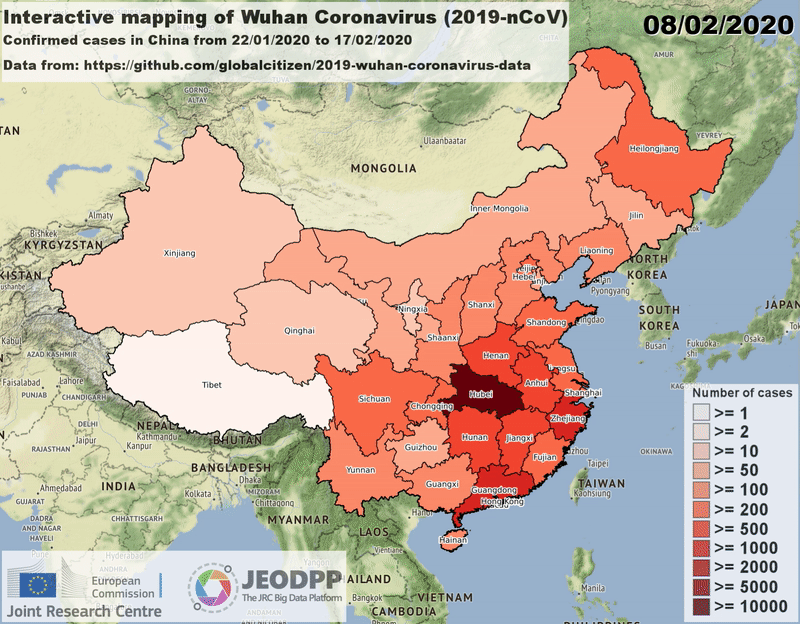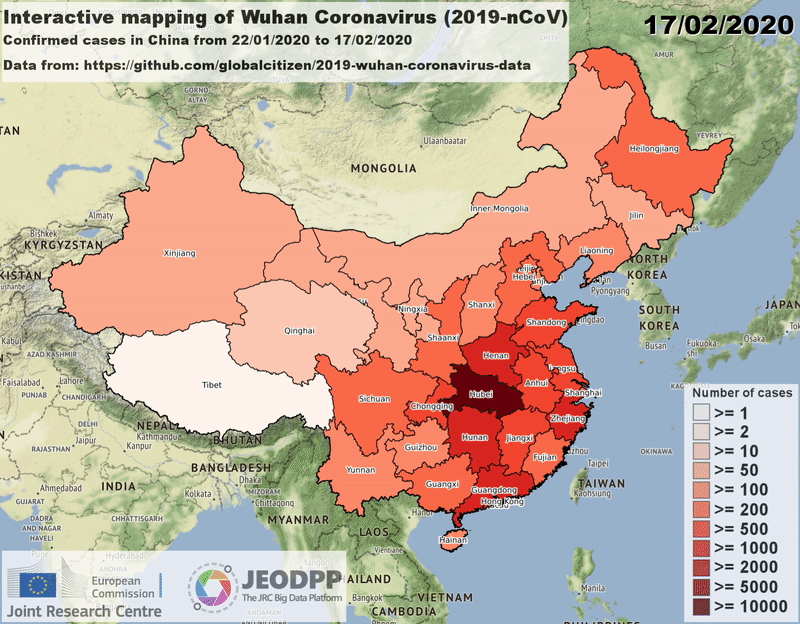
Creation and closure¶
-
Video.__init__(format, FilePath, lonmin=0.0, latmin=0.0, lonmax=0.0, latmax=0.0, zoom=0, DelayInMilliseconds=1000, FramesPerSecond=1)¶ Initialization of a Video instance
Args:
format(integer): format of the video: VIDEO_GIF, VIDEO_MP4 or VIDEO_WEBMFilePath(string): path of the video file to create.lonmin(float): minimum longitude of the geographic area in degrees (optional).latmin(float): minimum latitude of the geographic area in degrees (optional).lonmax(float): maximum longitude of the geographic area in degrees (optional).latmax(float): maximum latitude of the geographic area in degrees (optional).zoom(integer): zoom level in the range [1,18] (optional).DelayInMilliseconds(integer): time between frames in case of output to a GIF file (optional, default = 1000 = 1 second).FramesPerSecond(integer): number of frames to play for each second in case of output to a MP4 or WEBM video file (optional, default = 5).
-
Video.close()¶ Closes the output file and finalizes the video creation.
Settings¶
-
Video.setDelayInMilliseconds(DelayInMilliseconds=1000)¶ Set the delay in milliseconds between the frames in case of output to GIF format.
Args:
DelayInMilliseconds(integer): time between frames in case of output to a GIF file (optional, default = 1000 = 1 second).
-
Video.setFramesPerSecond(FramesPerSecond=1)¶ Set the number of frames to play for each second in case of output to MP4 or WEBM format.
Args:
FramesPerSecond(integer): number of frames to play for each second in case of output to a MP4 or WEBM video file (optional, default = 1).
-
Video.setExtentsAndZoom(lonmin, latmin, lonmax, latmax, zoom)¶ Set the geographic extent and the zoom level of the area to save in the video.
Args:
lonmin(float): minimum longitude of the geographic area in degrees (optional).latmin(float): minimum latitude of the geographic area in degrees (optional).lonmax(float): maximum longitude of the geographic area in degrees (optional).latmax(float): maximum latitude of the geographic area in degrees (optional).zoom(integer): zoom level in the range [1,18] (optional).
-
Video.setMap(map)¶ Set the geographic extent and the zoom level of the area to save in the video from the current viewport and zoon of a
Mapclass instanceArgs:
map(Map): An instance of aMapobject
-
Video.getWidth()¶ Returns the width of the video in pixels.
-
Video.getHeight()¶ Returns the height of the video in pixels.
Overlays¶
-
Video.overlayReset()¶ Resets the list of images to overlay to the frames of the video.
-
Video.overlayAddFile(FilePath, x, y, opacity=255)¶ Add a new image from a PNG file to overlay over the subsequent frames of the video
Args:
FilePath(string): path of the PNG image to overlay.x(integer): x starting position of the image on the video frames (0 = left border of the video).y(integer): y starting position of the image on the video frames (0 = top border of the video).opacity(integer): value of opacity to apply to the image (optional, default = 255)
-
Video.overlayAddImage(img, x, y, opacity=255)¶ Add a new image from a PIL (or Pillow) Image object to overlay over the subsequent frames of the video
Args:
img(PIL.Image): image to overlay.x(integer): x starting position of the image on the video frames (0 = left border of the video).y(integer): y starting position of the image on the video frames (0 = top border of the video).opacity(integer): value of opacity to apply to the image (optional, default = 255)
- Example:
Create a PIL.Image with a string of text and add as overlay to a Video frame.
Import of PIL Image, ImageDraw and ImageFont:
from PIL import Image, ImageDraw, ImageFont
Define a function that calculates the dimensions in pixels of a string rendered with a font:
# Returns the size (w,h) in pixels of a text when displayed with a font def getSize(txt, font): testImg = Image.new('RGB', (1, 1)) testDraw = ImageDraw.Draw(testImg) return testDraw.textsize(txt, font)
Set the font to be used from a local TrueType file and define some color constants:
fontname = './ariblk.ttf' # Arial Black text = 'Sample string' colorText = 'black' colorHalo = 'white' colorBackground = (255, 255, 255, 0)
Create the font and read the dimension in pixels:
font = ImageFont.truetype(fontname, 40) w,h = getSize(text, font)
Create the Image and draw the text on it using a halo effect:
img = Image.new('RGBA', (w+4, h+4), colorBackground) d = ImageDraw.Draw(img) d.text((4, 4), date, fill=colorHalo, font=font) d.text((2, 2), date, fill=colorText, font=font)
Add the img Image object as an overlay to the subsequent frames:
vo.overlayReset() vo.overlayAddImage(img, 0, 0, 255)
For a reference guide on Pillow classes and functions, see https://pillow.readthedocs.io/
Adding of frames¶
-
Video.addFrame(ip, dissolved=0)¶ Add a frame to the video. The graphic content of the frame can come from a single instance of the
ImageProcessclass of from a list of ImageProcess instances. In this latter case, all the ImageProcess instances are rendered one over the other (managing transparency) and the final image is added to the video.Args:
ip(ImageProcess or list of ImageProcess objects): single instance or list of instances of classImageProcessto be rendered ina a frame that will be added to the videodissolved(integer): number of intermediate frames to create from the previous frame to the one that is added in order to create a smooth transition (optional, default = 0).
Example:
Add to a frame the composition of a basemap and a VectorLayer with 5 dissolved frames:
pbase = Collection(collections.basemaps.Stamen.Terrain).process() pcountries = Collection(collections.BaseData.AdministrativeUnits.Europe.GISCO.Nuts1).process() vo.addFrame([pbase,pcountries], 5)